Construction and maintenance work at height carries risks that cannot be managed by structure alone. The stability of frames and platforms matters, yet worker protection depends just as much on the safety components fitted to those platforms. In many projects involving mobile scaffolding for sale finland, guardrails and toe boards are often viewed as secondary additions rather than essential elements. This perception can lead to unsafe practices, preventable accidents, and reduced confidence among workers operating above ground level.
Why Edge Protection Defines Scaffolding Safety?
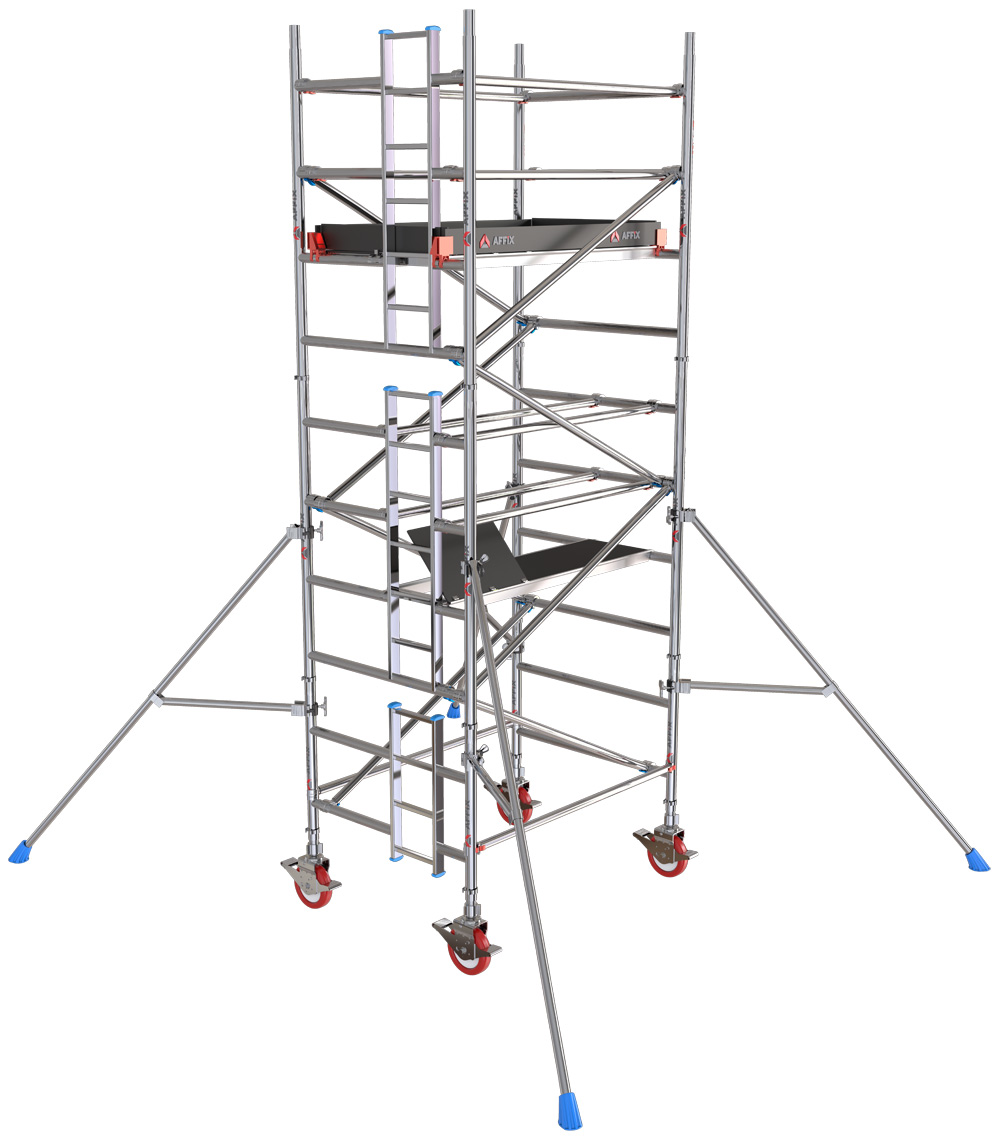
Mobile scaffolding is designed for movement, flexibility, and speed. These same qualities introduce unique safety challenges. When a tower is repositioned, when workers move laterally, or when tools are handled repeatedly, exposure to open edges increases. Guardrails and toe boards define the boundary between a secure working zone and open space.
Without clear physical barriers, workers rely on balance and awareness alone. Fatigue, distraction, or uneven surfaces can quickly turn minor missteps into serious falls. Edge protection converts a platform from a simple standing surface into a controlled work environment.
Guardrails as the First Line of Fall Prevention
Guardrails serve a simple but powerful purpose: they stop people from falling. Their presence provides both physical restraint and psychological reassurance. Workers instinctively adjust their movement when a solid rail is within reach, reducing overextension and sudden shifts in posture.
Properly installed guardrails include top rails, mid rails, and secure connections to vertical standards. This layered approach ensures that even if a worker stumbles or leans unexpectedly, the structure absorbs the force rather than allowing a fall.
In mobile scaffolding, where height can change frequently, guardrails must remain effective regardless of platform level. Systems that allow guardrails to be repositioned easily encourage consistent use instead of shortcuts.
Toe Boards and the Hidden Risk of Falling Objects
While falls from height receive much attention, falling objects present an equally serious hazard. Tools, materials, and debris dropped from scaffolding can injure workers below or damage property. Toe boards address this risk by creating a raised edge along the platform perimeter.
Toe boards prevent small items from sliding off the platform during routine tasks. They also help contain debris generated during drilling, cutting, or surface preparation. This containment reduces the need for exclusion zones below, allowing other trades to work safely nearby.
The Relationship Between Guardrails and Toe Boards
Guardrails and toe boards function best as a combined system rather than isolated components. Guardrails protect the worker, while toe boards protect everyone else on site. Together, they create a defined working envelope that supports safe movement and material handling.
This relationship becomes especially important on mobile scaffolding, where platforms may be narrower than fixed structures. Limited space increases the chance of accidental contact with edges, making comprehensive edge protection essential.
Mobile Scaffolding and Movement-Related Risks
Unlike static scaffolding, mobile towers are designed to be moved frequently. Even when castors are locked during use, the knowledge that the structure can roll influences how workers behave. Sudden shifts in weight, tool placement near edges, and frequent repositioning all increase risk.
Guardrails provide a consistent reference point during these movements. Workers can maintain three points of contact more easily when rails are within reach. Toe boards ensure that equipment remains secure during relocation, preventing tools from falling as the tower is moved.
Impact on Worker Confidence and Performance
Safety equipment does more than prevent accidents; it shapes how people work. When guardrails and toe boards are present and properly installed, workers approach tasks with greater confidence. This confidence translates into smoother movements, better posture, and more precise work.
On the other hand, platforms without edge protection create tension. Workers move cautiously, hesitate to reach certain areas, or rush tasks to minimize time at height. These behaviors reduce work quality and increase the likelihood of mistakes.
Regulatory Expectations and Practical Compliance
Most safety regulations require guardrails and toe boards on scaffolding platforms above specific heights. These rules exist because data consistently shows reduced accident rates where edge protection is used correctly.
Compliance, however, is not just about meeting minimum standards. Well-planned scaffolding incorporates guardrails and toe boards as integral parts of the system rather than optional accessories. This approach simplifies inspections and avoids last-minute modifications that disrupt workflow.
Common Scenarios Where Edge Protection Matters Most
Certain tasks increase reliance on guardrails and toe boards due to movement patterns and tool use. Examples include:
- Electrical installation requiring lateral movement
- Painting and coating with frequent repositioning
- Mechanical maintenance involving handheld equipment
- Window installation near open edges
- Cleaning tasks with water and slippery surfaces
In each scenario, edge protection supports safe positioning and reduces reliance on personal balance alone.
Design Considerations for Effective Guardrails
Not all guardrails offer the same level of protection. Height, spacing, and rigidity all influence effectiveness. Top rails should align with ergonomic standards, allowing workers to lean slightly without excessive pressure. Mid rails prevent slips through the lower opening, while secure fixings maintain stability during use.
In mobile scaffolding, guardrails must remain rigid even as the structure is moved and reassembled. Systems that rely on simple locking mechanisms encourage correct installation and reduce assembly errors.
Toe Board Height and Platform Coverage
Toe boards must be tall enough to stop tools but not so tall that they create trip hazards. Consistent height along the entire platform perimeter ensures predictable protection. Gaps or missing sections undermine effectiveness and invite unsafe practices.
Full perimeter coverage matters, even on sides that seem less exposed. Tools can roll unexpectedly, especially on slightly uneven platforms. Continuous toe boards remove this uncertainty.
Influence on Site Organization
Edge protection affects more than the immediate platform. When toe boards contain tools and materials, the area below becomes safer. This allows better coordination between trades and reduces the need for barriers or warning zones.
Improved organization benefits supervisors as well. Clear boundaries make it easier to assess compliance during site walks and address issues before they escalate.
Training and Habit Formation
Workers trained on scaffolding systems with integrated guardrails and toe boards develop safer habits. They learn to rely on proper equipment rather than improvisation. Over time, these habits carry across different sites and projects.
When edge protection is inconsistent, training loses effectiveness. Workers may become accustomed to missing components and fail to recognize unsafe conditions elsewhere.
Maintenance and Inspection of Safety Components
Guardrails and toe boards require regular inspection, especially on mobile systems that are assembled and dismantled frequently. Bent rails, loose fixings, or damaged boards compromise protection.
Routine checks should focus on:
- Secure attachment points
- Straightness and rigidity of rails
- Continuous toe board coverage
- Compatibility with platform dimensions
Maintaining these components ensures that safety features perform as intended throughout the project lifecycle.
Weather and Environmental Factors
Outdoor work introduces wind, rain, and temperature changes. Wet platforms increase slip risk, making guardrails essential for balance support. Wind can move loose materials, highlighting the importance of toe boards.
In colder conditions, gloves and layered clothing reduce dexterity. Solid edge protection compensates by providing physical barriers that do not rely on precise hand movements alone.
Psychological Boundaries and Spatial Awareness
Humans respond strongly to visible boundaries. Guardrails and toe boards create a clear visual frame that helps workers judge space and distance. This spatial awareness reduces missteps, especially on elevated platforms where depth perception can be distorted.
Clear boundaries also discourage unsafe behaviors such as standing on platform edges or placing tools near drop zones.
Cost Versus Consequence
Some view guardrails and toe boards as additional costs or setup time. This perspective overlooks the financial impact of accidents, delays, and damaged equipment. A single dropped tool can halt work, trigger investigations, and damage client trust.
Investing in proper edge protection reduces these risks and supports uninterrupted operations. Over time, this reliability outweighs any perceived savings from omission.
Integration With Personal Protective Equipment
Edge protection complements personal protective equipment rather than replacing it. Harnesses, helmets, and footwear all play roles, but they are most effective when combined with physical barriers.
Guardrails reduce reliance on fall arrest systems, while toe boards protect workers who may not be directly involved in elevated tasks. This layered safety approach reflects best practice across construction and maintenance environments.
Situations Where Shortcuts Are Tempting
Time pressure, small tasks, or frequent repositioning can tempt crews to skip guardrails or toe boards. These shortcuts often occur during quick adjustments or brief jobs.
Recognizing these moments and reinforcing standards prevents normalization of risk. Consistent installation sends a clear message that safety applies regardless of task duration.
Benefits That Extend Beyond Safety
While prevention is the primary goal, guardrails and toe boards offer additional benefits:
- Improved worker confidence and morale
- Cleaner platforms with organized tools
- Reduced damage to materials below
- Smoother coordination between teams
- Stronger safety culture on site
These outcomes contribute to overall project success.
Planning for Edge Protection From the Start
Effective scaffolding planning includes edge protection at the earliest stage. Platform dimensions, access points, and task requirements should all inform guardrail and toe board placement.
Early planning avoids last-minute adjustments that disrupt work or create gaps in protection. It also ensures compatibility between components and platform layout.
Mobile Scaffolding in Confined or Shared Spaces
In indoor environments such as warehouses or commercial buildings, mobile scaffolding often operates near walkways or occupied areas. Toe boards become particularly important in these settings, preventing objects from falling into active zones.
Guardrails help workers maintain safe posture when navigating around obstacles or structural features within confined spaces.
Long-Term Influence on Safety Culture
Consistent use of guardrails and toe boards shapes how teams perceive risk. When edge protection is standard practice, unsafe setups stand out immediately. This awareness encourages peer accountability and early intervention.
Over time, this culture reduces incident rates and supports professional standards across projects.
Conclusion
Guardrails and toe boards are not accessories; they are defining elements of safe mobile scaffolding. They protect workers, safeguard those below, and support confident, efficient work at height. In mobile systems where movement and flexibility increase exposure, their role becomes even more critical.
By treating edge protection as an integral part of scaffolding design and use, contractors and site managers create safer environments that support productivity, quality, and long-term reliability.